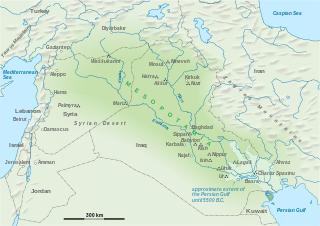
The territory.
Mesopotamia, comes from Greek and it means, the land between two rivers: Euphrates and Tigris. Both of them share several characteristics:
We can distinguish two large regions:- Their source is located in the Armenian mountains.
- They flow parallel for a large part of their course.
- Both flow in the Persian Gulf.
- During the spring its water overflows their banks and fertilise the land.
- Lower Mesopotamia or Chaldea, located in the south and was occupied by the Sumer and Akkadian civilisations.
- Upper Mesopotamia or Assiria., located in the north.
Historical evolution.
Chronology: from 3.500 B. C. with the apparition of the first city-states to 539 B. C. with the conquest of Babylon by the Persian Empire.We can divide its history into periods of time defined by the people which controlled the region. We can distinguish two stages:
The first city-states.
The mesopotamian civilisation started around 3.500 B. C, when a people of unknown origin, the sumerians established themselves in Lower Mesopotamia.
The sumerians extended the crop growing areas with irrigation thanks to:
- the use of irrigation canals
- the use of dykes and walls to control the rivers periodic rises.
Irrigation canals, Iraq. Source: Nevit Dilmen stitched by Marku1988
As a consequence, a group of independent city-states appeared (Ur, Uruk, Lagash and Eridu). A city-state is a city which controls its surrounding territory and is politicaly and economicaly independent. These cities fought against each other.
 |
| Ruins of Ur. |
The first empires.
From 2.300 B. C., Mesopotamia was dominated by other peoples:
- The Akkadians (24th century-23 th century B. C) invaded the sumerian cities and a empire was established by its king Sargon I. Its capital was Akkad.
- The Babylonians (18th century-16th century B. C.) established a empire with capital in Babylon, located between sumer and Akkad. Its most important king was Hammurabi who created the first legal code.
- The Assyrians (16th century-13th century B. C. and 10th century-8th century B. C.) a warlike people from upper Mesopotamia. Its capital cities were Assur and Niniveh. The most important king was Ashunasirpal II (9th century B. C.).
- The Persians who conquered Mesopotamia in 539 B. C., turning it into one province of their empire.
Este blog es muy util me ayuda a estudiar mejor para un examen
ResponderEliminar