 |
| For exmple, in a flat surface the sum of the angles of a triangle always sums 180º, but in a sphere always sums MORE than 180º. |
Maps and their elements.
A map is a simplified representation of the Earth's spherical surface, or a part of it, depicted on a flat surface.
In order to make a map, cartographers need three elements:a system of projection, a scale and set of standard sings or legend.
System of projection.
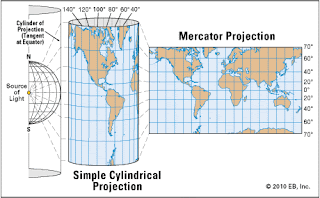
-A system of projection is a system that allow us to represent a spherical surface on a flat surface, translating the network of parallels and meridians.There are three main types of systems of projection:
- cylindrical projection, transfers the grid of parallels and meridians into a cylinder. It is the best method to represent the low latitudes the low latitudes between the Equator and the tropics.
- Conic or conical projection, transfer the grid of parallels and meridians into a cone. It is the best method to represent the mid-latitudes.

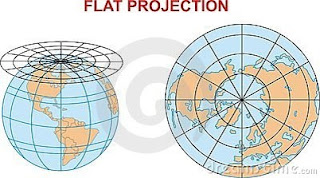
- Azimuthal or plane projection, transfers the grid of parallels and meridians into a flat surface. It is the most appropiate method to represent the polar areas.
-Scale is the method that we use to indicate the relation between a distance drawn on the map and the same distance on the ground. There are two types of scale:
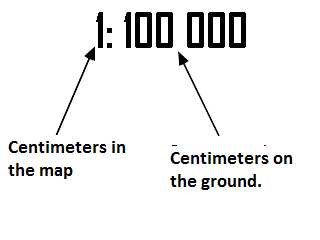
- Numerical scale. It is indicates the relationship between the unit used to make the map and the reality. Usually a fraction is used. the numerator indicates the distance on the map and the denominator its equivalent on the ground.
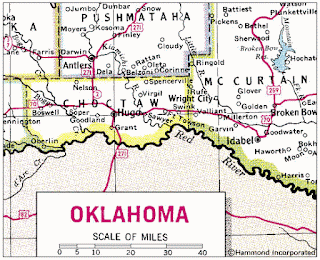
- Graphic scale.It consists of a straigh line divided into segments. Every segment is equivalent to a real distance in the ground.
Legend or key of the map: is a set of colours, standar signs or symbols used to represent reality in the map in a simplified form.
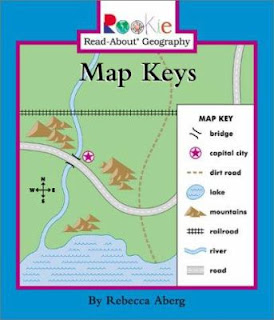
Types of maps:
There are two types of maps:
- Topographic or basic maps: represent in detail the physical and human aspects of the territory.
- Thematic maps: represent a specific geographica aspect.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario